The Link Between Chronic Dieting and Hormonal Imbalance
July 29, 2025
Yogurt & Berry Bowl with Flax
August 3, 2025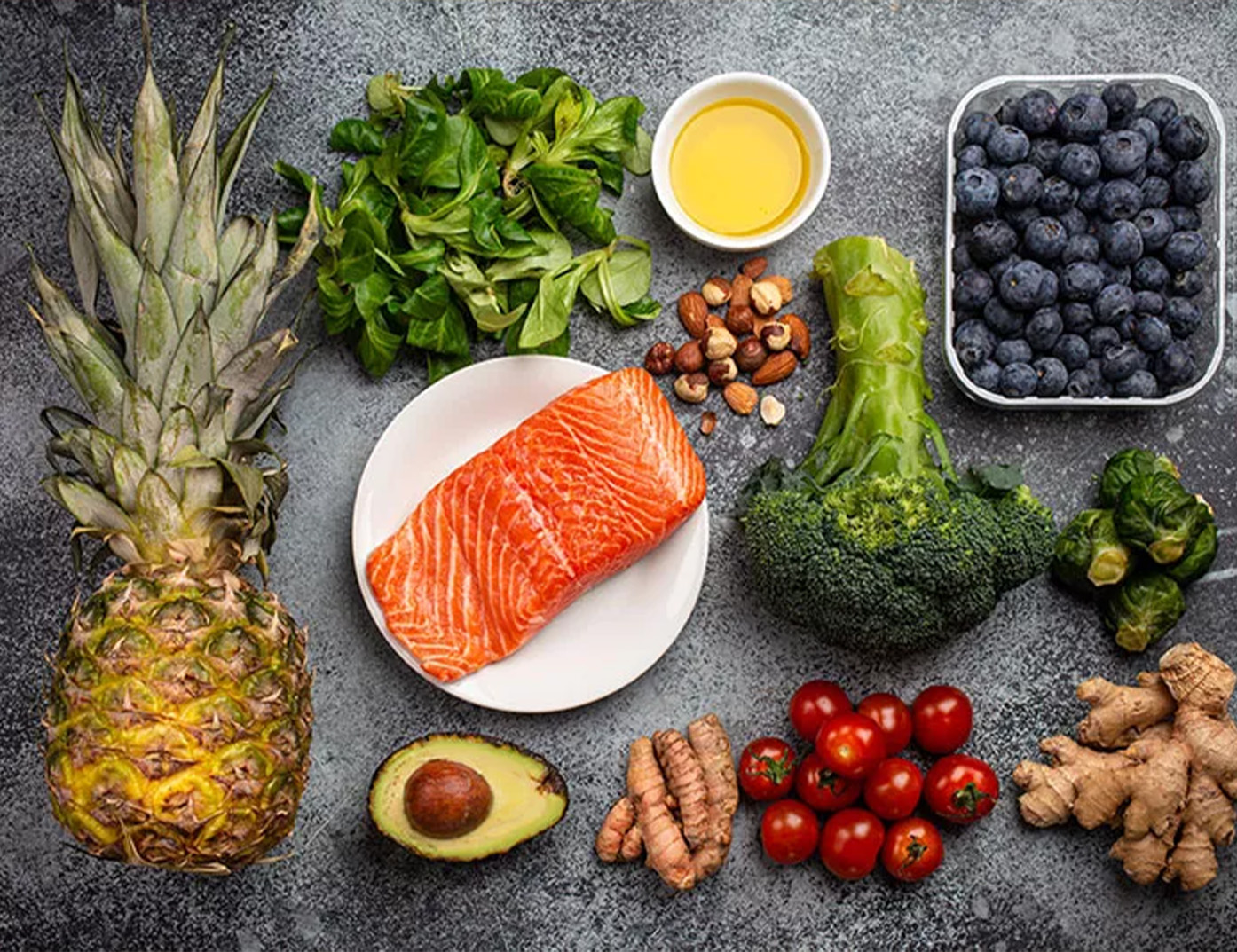
The Silent Saboteurs of Your Health and Weight Loss Goals
Inflammation is your body’s natural response to injury or infection. It’s how the immune system protects and heals. But when inflammation becomes chronic, it silently contributes to a wide range of health issues—from fatigue and joint pain to obesity, insulin resistance, and even heart disease.
What many people don’t realize is that their daily diet might be fueling this hidden fire. In this article, we’ll uncover the most common dietary triggers of chronic inflammation and how to make better choices to support long-term health and fat loss.
What Is Chronic Inflammation?
Unlike acute inflammation (like swelling after an injury), chronic inflammation is low-grade, persistent, and often symptomless—until the damage is already done. It can:
- Disrupt hormone balance
- Slow metabolism
- Increase fat storage
- Damage tissues and organs
- Elevate stress hormones like cortisol
And yes, it can sabotage your weight loss efforts, no matter how well you exercise.
Top Hidden Inflammation Triggers in Your Diet
1. Refined Sugar and High-Fructose Corn Syrup
Sugar is one of the most well-documented drivers of inflammation. It spikes blood sugar, leading to insulin resistance, which fuels fat gain and inflammatory cytokine production.
Foods to watch out for:
- Soda and sweetened drinks
- Packaged desserts
- Breakfast cereals
- “Low-fat” foods that compensate with sugar
Tip: Replace added sugars with natural sources like fruit, and read ingredient labels carefully—even savory items may contain hidden sugars.
2. Refined Carbohydrates and White Flour
Refined carbs—such as white bread, pasta, and pastries—digest quickly and flood your bloodstream with glucose, similar to sugar. They also feed harmful gut bacteria, which in turn produce toxins that trigger inflammation.
Better choice: Switch to whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats.
3. Vegetable Oils High in Omega-6
While omega-6 fatty acids aren’t inherently bad, the imbalance between omega-6 and omega-3 in the modern diet is a problem. Vegetable oils such as soybean, corn, sunflower, and canola oil are high in omega-6 and promote inflammation when not balanced with omega-3s.
Found in:
- Fast food
- Packaged snacks
- Salad dressings
- Margarine
Tip: Use anti-inflammatory fats like olive oil, avocado oil, flaxseed, and fatty fish (salmon, sardines) to rebalance.
4. Processed Meats
Bacon, sausages, deli meats, and hot dogs contain nitrates, preservatives, and compounds formed during processing and cooking (like AGEs—advanced glycation end products) that trigger inflammation.
They’ve also been linked to increased risk of heart disease and cancer.
Alternative: Choose fresh, lean meats or plant-based proteins like lentils, chickpeas, and tofu.
5. Artificial Additives and Preservatives
Many food colorings, sweeteners (like aspartame), and chemical preservatives have been shown to irritate the gut lining, disrupt microbiome balance, and increase inflammatory responses.
Check for:
- Sodium benzoate
- Monosodium glutamate (MSG)
- Artificial dyes (e.g., Red 40, Yellow 5)
Tip: Stick to whole foods with short ingredient lists.
6. Gluten and Dairy (for Some People)
Gluten and casein (a protein in dairy) are not inflammatory for everyone—but for those with sensitivities or intolerances, they can increase gut permeability (“leaky gut”) and lead to chronic immune activation.
Common signs:
- Bloating
- Fatigue
- Skin breakouts
- Brain fog
If you suspect an issue, consider an elimination diet or speak with a healthcare professional.
7. Alcohol
Even moderate alcohol intake can increase gut permeability, impair liver detoxification, and raise inflammation markers like CRP (C-reactive protein).
Chronic alcohol use is also linked with hormonal imbalance, weight gain, and fatty liver.
Tip: Limit alcohol to occasional use, and hydrate well when you do consume it.
How Inflammation Affects Weight Loss
Inflammation affects fat loss in multiple ways:
- Increases insulin resistance, making fat storage more likely
- Raises cortisol, which promotes belly fat
- Slows thyroid function, decreasing metabolic rate
- Disrupts hunger hormones, leading to cravings and overeating
In short, even if you’re eating less, chronic inflammation can keep your body in “fat-storing mode.”

Anti-Inflammatory Diet Tips
Instead of focusing on what to eliminate, think about what to add. A diet that calms inflammation includes:
✅ Leafy greens and cruciferous vegetables
✅ Berries, grapes, and citrus fruits
✅ Omega-3-rich foods (chia, flax, walnuts, fish)
✅ Herbs and spices (turmeric, ginger, garlic)
✅ Green tea
✅ Adequate hydration
✅ Fermented foods for gut health (kimchi, yogurt, kefir)
Conclusion: Listen to Your Body
You don’t need to go on an extreme cleanse or fear food. But by becoming aware of the hidden inflammatory triggers in your everyday meals, you can make better choices that support both your health and your weight goals.
Start small:
- Replace processed snacks with whole fruits
- Use olive oil instead of vegetable oil
- Cook more at home and read labels
Healing inflammation isn’t a crash fix—it’s a consistent, kind approach to nourishing your body for the long term.